Index Of The Blog
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS

Cloud services are one of the best internet innovations. Instead of purchasing expensive software, set up platforms, or hardware along with the never-ending cost of maintenance and updates, cloud computing services allow you to pay a monthly fee to use complex services. IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
Depending on the services you need and the level of control and flexibility you’re after, there’s a cloud computing model for you.
So, what is infrastructure as a service?
Why You Need Cloud Services
Cloud computing services allow you to flexibly scale your work, whether professional or personal, without the hassle of buying and maintaining your own resources.
Cloud services make tools that rely on expensive and complex resources available to the average user instead of exclusive to large corporations. They can solve many of your issues and save time, but only when you chose the right option. IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS.
The most common types of cloud services you might be most curious about are IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS. So, what’s the difference between the three and which one should you invest in?
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
To start, you need to understand what each acronym means before delving into what separates and connects them.
- IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service.
- PaaS: Platform as a Service.
- SaaS: Software as a Service.
IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS aren’t entirely separate concepts. They simply work on different levels of the same structure.
When you own the hardware, you need to manage all the background parts and operations that lead to the final result. That means having to build and manage your own infrastructure, from storage and servers to virtualization, and so on.
After setting up the infrastructure, you need a running platform to work with. A platform includes the tools, databases, and applications your operation requires. Software is the last layer that helps you accomplish a specific task efficiently.
SaaS: What is Software as a Service?
The introduction gave away that “SaaS” stands for “Software as a Service.”
While it’s not a commonly used term, you can think about this as being separate from “Software as a Good.” Just like goods and services in other aspects of your life, digital goods can be seen as something that you pay for once and consume, while a service is something that you pay someone else to do for you as you need it done.
There’s another way to illustrate SaaS if you’re old enough to take a trip down memory lane into any time before, say, Y2K or a little later. You needed the most recent edition of a word processor, so you went to the nearest tech store and purchased it on a disk. You could then return home and install it on your computer.
An easy way to think about SaaS is as any service that you access online and/or pay a subscription fee for instead of downloading from a purchased hardcopy. Even the internet itself can arguably be viewed as SaaS, now that we’re not buying AOL disks to connect our computers to the internet for limited periods of time.
If we think about things that way, just about anything that we do with computers that used to be “software as a good” (internet, word processors, streaming media, games, antivirus software, etc.) is now under the umbrella of SaaS.
So far, this article has talked about how most consumers encounter SaaS. Businesses can encounter SaaS in some different use cases, though the basic idea is the same. SaaS solutions that businesses and organizations may encounter include web hosting, event registration, payment systems, and other services.
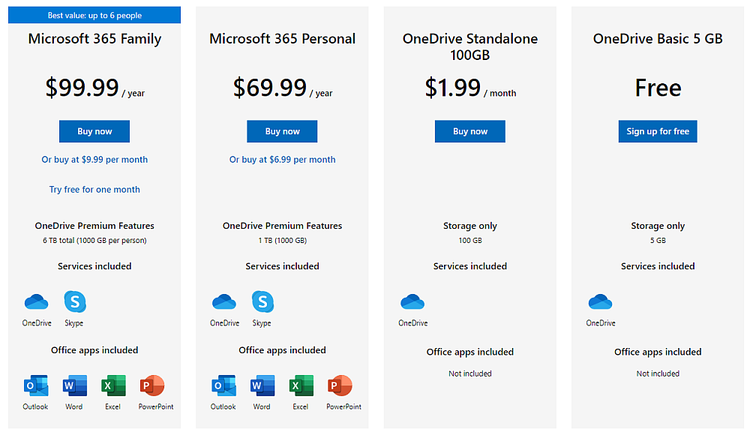
SaaS Subscription Services
Adobe’s suite of editing software is one of the best examples of subscription-based SaaS. These and other subscription-based SaaS applications involve paying to renew the service regularly as it is being used.
Benefits and Drawbacks of SaaS
The benefits and drawbacks of SaaS compared to “older” models are largely subjective and depend on what services you use and how you use them. If you don’t care for the benefits, or there are drawbacks related to your use case, many services offered through SaaS can still be purchased and downloaded like in the old days.
Benefits of SAAS
- SaaS Is Cheaper and More Efficient: Because SaaS is delivered over the internet rather than through a physical disk and associated packaging, providers can offer it at lower prices. Not to mention you don’t need to physically go to the store to buy the most recent version of your favorite word processor or media editor. IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
- Benefit: SaaS and the Cloud: As addressed, being offered through the internet and the cloud offers a huge additional benefit to SaaS solutions. Perhaps the biggest of these is being able to access applications and documents from anywhere.
In the days before OneDrive, you couldn’t access a document from your home computer and your office computer without either emailing it back and forth to yourself or carrying the document from place-to-place on an external storage device.
Drawbacks of SaaS
- SaaS and the Cloud: One of the biggest drawbacks to SaaS is that because many SaaS solutions are offered online, they require internet connectivity. This means that some services may not be available without the internet, but it may also come with security concerns.
As will be covered in a moment, one of the huge benefits of SaaS and cloud services is that files are available from anywhere. This can mean trusting potentially sensitive information in the hands of the likes of Google. It can also mean that if your internet provider or cloud service provider has technical difficulties, you can be locked out of your paid platforms. - Scale and Pricing Options: One of the potential drawbacks of SaaS has to do with their subscription-based pricing models. These often force the user into price tiers. Getting services that you need may mean needing to pay for services or storage space that you don’t. For the SaaS applications that most users are likely to encounter, this is overcome in two main ways.
First, as we’ve seen, the most common SaaS providers have a free tier that includes basic services and more storage than most people will ever need. After that, special users or organizations can pay for additional features as needed. Second, organizations or users requiring additional services usually have multiple price tiers or custom package options.
PaaS: Platform as a Service
What is Platform as a Service?
Often used by software developers and engineers, PaaS works as a building ground for software, applications, and framework testing. Managing both your data and applications allows for considerable flexibility without overwhelming you with server and network management, which your service provider handles.
Similar to SaaS, PaaS is delivered online through public, private, or hybrid cloud servers. The different cloud options allow for more flexibility and customization when it comes to the final product. For example, the service provider entirely controls and maintains public cloud PaaS. On the other hand, private cloud PaaS requires more participation and effort on your end.
There are a lot of uses for PaaS models. The slightly more complex and less known Google App Engine is a good PaaS example, as well as the better known Windows Azure and LongJump are some examples of PaaS providers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PASS
The core advantages of PaaS (Platform as a Service) are:
- Reduced costs — you cut initial expenses since you don’t have to buy equipment, set up the stack and maintain it; moreover, you will not pay for unforeseen expenses in case of downtime.
- Improved time to market — app development is speeded up due to numerous available automated tools and ready-to-use infrastructure.
- Continuous updates — PaaS experts perform all the necessary updates and you get them automatically.
- Scalability — a default scaling mechanism can automatically release additional resources for your needs.
- Freedom of action — you manage programs and services you create by yourself.
Disadvantages of PaaS (Platform as a Service) are:
- Dependency on the vendor — provider’s functional capabilities, speed and reliability will govern your business, whether you like it or not.
- Compatibility of existing infrastructure — legacy solutions are supposed to work but not all of them can be compatible with new infrastructure, which will cause troubles.
- Security risks — your sensitive data may be threatened since multiple users have access to PaaS resources deployed in a public cloud environment.
IaaS: Infrastructure as a Service
What is Infrastructure as a Service?
IaaS offers the minimum resources, setting up only the necessary infrastructure, leaving the building and customization to you. While adding the other layers might require a lot of effort, it’s the most flexible and easily-scalable cloud service model between the three.
With IaaS, you basically rent servers, networks, virtualization, and storage along with their maintenance and management. However, instead of simply accessing them like a web application, IaaS providers often operate through a dashboard or an API, giving you maximum control.
As you can still access your data servers remotely, your work model mostly depends on virtual data centers and virtual servers instead of on-site, physical ones. Some IaaS examples to consider are Amazon Web Services, Google Compute Engine, and VMware.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PASS
Benefits or advantages of IaaS
Following are the benefits or advantages of IaaS:
- It allows full control of computing resources through administrative access to VMs (Virtual Machines).
- Hence customers can run anything, choose to automate provisioning or build their own VM.
- It offers flexible and efficient renting of computer hardware.
- It offers portability and interoperability with legacy applications.
- It simplifies integration with enterprise infrastructure.
- The customers do not have to worry about cost and maintenance while running its own virtual infrastruture (instead of its own hardware). IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS.
Drawbacks or disadvantages of IaaS
Following are the drawbacks or disadvantages of IaaS:
- It is most expensive service as customer is leasing a tangible resource. The provider can charge for every cycle, bit of RAM or disk space used.
- Customers are responsible for backups and all other aspects of VM management.
- Customers or users do not have any control over server used or its geographical location.
- Compatibility with legacy security vulnerabilities
- Virtual machine sprawl
- Data erase practices
- Robustness of VM level isolation
The Limitations of Cloud Services
While different cloud services offer different benefits and have varying demands, they all share a set of limitations and disadvantages that could be complete deal-breakers to some.
- Lack of Control: Having a third-party service provider manage a big chunk of your operations is a double-edged sword. While it might take a lot of weight off your shoulders, it also drastically reduces the level of control you have over your resources.
- Downtime: Downtime is unavoidable, even with the high-end service providers. Not having control over your infrastructure, platform, or primary software could be disastrous for any period of time. After all, downtime leaves you stranded with no resources or tools to work with. IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS.
- Connection Issues: Similar to downtime, internet connection issues could have devastating consequences since all services are provided remotely via the web.
Connection issues, either on yours or the service provider’s end, are bound to occur, lasting anywhere from a few minutes to hours and days. Not having your resources on-site means all of your work and operations come to a halt until you or your provider fix the connection issue, as backup plans can only take you so far. IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS. - Privacy and Security: By using cloud services, you’re handing a significant portion of your data to off-site locations. In addition to reduced privacy, you must trust your service provider with your data’s security. IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS.
After all, it’s up to them to provide adequate protection against cyberattacks and data leaks, which could harm your reputation and finances even if the attack wasn’t your immediate fault.
Making the Most of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing services are proving to be a crucial part of today’s technical operations. They’re easy to use and save you a lot of time, effort, and resources in the long run, making complex tech more widely available and easier to use.
Making the most of cloud service means understanding the pros and cons and each service type and service provider. You need to determine which works best for you now and would be able to grow alongside your evolving needs.